RECENT ARTICLES
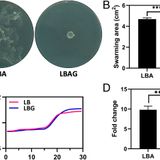
Bacterial-induced pH shifts link individual cell physiology to macroscale collective behavior
Edited by Bonnie L. Bassler, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, and approved February 16, 2021 (received for review July 8, 2020)Individual cells within a community often need to respond to changing environmental conditions at the population level. Accordingly, bacteria have evolved a large array of regulatory mechanisms that enable them to quickly reprogram behavior in a coordinated manner. Unraveling these mechanisms provides valuable information regarding collective behavior in the bacterial world. Herein, we show that by modulating the environmental pH levels, bacterial colonies...…Edited by Bonnie L. Bassler, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, and approved February 16, 2021 (received for review July 8, 2020)Individual cells within a community often need to respond to changing environmental conditions at the population level. Accordingly, bacteria have evolved a large array of regulatory mechanisms that enable them to quickly reprogram behavior in a coordinated manner. Unraveling these mechanisms provides valuable information regarding collective behavior in the bacterial world. Herein, we show that by modulating the environmental pH levels, bacterial colonies...WW…
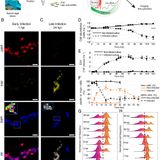
Visualizing active viral infection reveals diverse cell fates in synchronized algal bloom demise
Edited by James L. Van Etten, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE, and approved February 1, 2021 (received for review October 15, 2020)Despite years of research in aquatic virology, we remain unable to estimate viral-induced mortality in the ocean and, consequently, to resolve viral impact on nutrient fluxes and microbial dynamics. Here, we assess active infection in algal single cells by subcellular visualization of virus and host transcripts, revealing the coexistence of infected and noninfected subpopulations. We revisit major assumptions of a giant virus’ life cycle: cells can produce...…Edited by James L. Van Etten, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE, and approved February 1, 2021 (received for review October 15, 2020)Despite years of research in aquatic virology, we remain unable to estimate viral-induced mortality in the ocean and, consequently, to resolve viral impact on nutrient fluxes and microbial dynamics. Here, we assess active infection in algal single cells by subcellular visualization of virus and host transcripts, revealing the coexistence of infected and noninfected subpopulations. We revisit major assumptions of a giant virus’ life cycle: cells can produce...WW…
- Total 2 items
- 1