RECENT ARTICLES
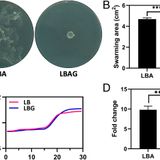
Bacterial-induced pH shifts link individual cell physiology to macroscale collective behavior
Edited by Bonnie L. Bassler, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, and approved February 16, 2021 (received for review July 8, 2020)Individual cells within a community often need to respond to changing environmental conditions at the population level. Accordingly, bacteria have evolved a large array of regulatory mechanisms that enable them to quickly reprogram behavior in a coordinated manner. Unraveling these mechanisms provides valuable information regarding collective behavior in the bacterial world. Herein, we show that by modulating the environmental pH levels, bacterial colonies...…Edited by Bonnie L. Bassler, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, and approved February 16, 2021 (received for review July 8, 2020)Individual cells within a community often need to respond to changing environmental conditions at the population level. Accordingly, bacteria have evolved a large array of regulatory mechanisms that enable them to quickly reprogram behavior in a coordinated manner. Unraveling these mechanisms provides valuable information regarding collective behavior in the bacterial world. Herein, we show that by modulating the environmental pH levels, bacterial colonies...WW…

A towering genome: Experimentally validated adaptations to high blood pressure and extreme stature in the giraffe
The suite of adaptations associated with the extreme stature of the giraffe has long interested biologists and physiologists. By generating a high-quality chromosome-level giraffe genome and a comprehensive comparison with other ruminant genomes, we identified a robust catalog of giraffe-specific mutations. These are primarily related to cardiovascular, bone growth, vision, hearing, and circadian functions. Among them, the giraffe FGFRL1 gene is an outlier with seven unique amino acid substitutions not found in any other ruminant. Gene-edited mice with the giraffe-type FGFRL1 show...…The suite of adaptations associated with the extreme stature of the giraffe has long interested biologists and physiologists. By generating a high-quality chromosome-level giraffe genome and a comprehensive comparison with other ruminant genomes, we identified a robust catalog of giraffe-specific mutations. These are primarily related to cardiovascular, bone growth, vision, hearing, and circadian functions. Among them, the giraffe FGFRL1 gene is an outlier with seven unique amino acid substitutions not found in any other ruminant. Gene-edited mice with the giraffe-type FGFRL1 show...WW…
- Total 2 items
- 1